Health Considerations and Dietary Implications: Mozzarella Cheese Sticks Nutrition Facts

Mozzarella cheese sticks nutrition facts – The seemingly innocent mozzarella cheese stick holds a mirror to our relationship with food, reflecting both pleasure and potential pitfalls. Understanding its nutritional composition allows us to cultivate a mindful approach to eating, aligning our choices with our overall well-being. This exploration delves into the potential health effects of excessive consumption and the suitability of this popular snack within various dietary contexts.The abundance of saturated fat and sodium in mozzarella cheese sticks, if consumed in excess, presents a potential pathway to health challenges.
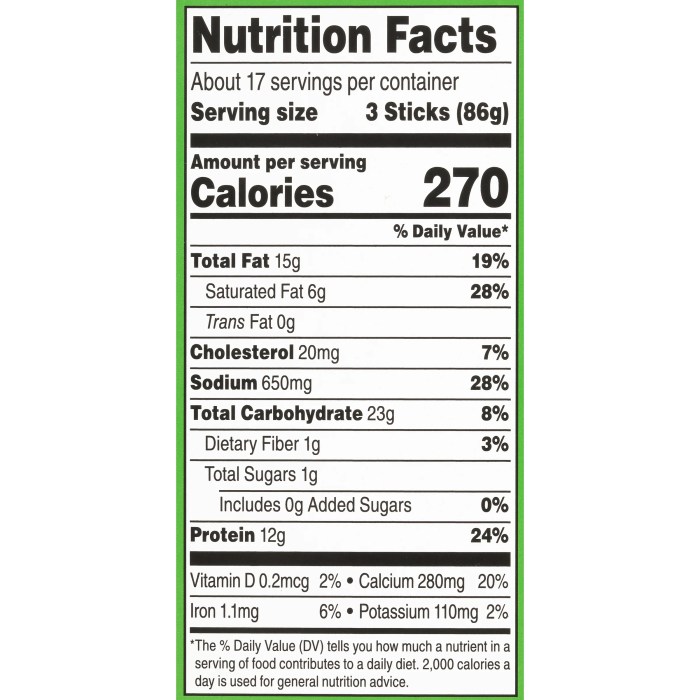
Saturated fat contributes to elevated cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Similarly, a high sodium intake can lead to hypertension and water retention, placing strain on the heart and kidneys. Moderation, therefore, is key to enjoying this treat without compromising long-term health.
Saturated Fat and Sodium Intake, Mozzarella cheese sticks nutrition facts
Excessive consumption of mozzarella cheese sticks, due to their high saturated fat and sodium content, can negatively impact cardiovascular health. Studies consistently link high saturated fat intake to increased LDL (“bad”) cholesterol, a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke. Similarly, high sodium intake elevates blood pressure, increasing the risk of hypertension, kidney disease, and other cardiovascular complications.
The recommended daily intake of saturated fat and sodium varies depending on individual factors and overall dietary patterns, but exceeding these limits through frequent consumption of mozzarella cheese sticks can pose significant health risks. For example, a single serving of cheese sticks might contain a significant portion of the recommended daily sodium intake, making it crucial to be mindful of portion sizes and overall dietary balance.
Dietary Restrictions and Health Conditions
Mozzarella cheese sticks present challenges for individuals with specific dietary restrictions. For those with lactose intolerance, the significant lactose content can trigger digestive discomfort, including bloating, gas, and diarrhea. Individuals with high cholesterol should exercise caution, limiting their consumption due to the saturated fat content. A mindful approach involves considering alternatives like dairy-free cheese sticks or reducing portion sizes to manage these health concerns.
It is advisable for individuals with such conditions to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine appropriate consumption levels or suitable alternatives.
Mozzarella cheese sticks, those crispy, golden delights, often pack a surprising caloric punch. Understanding their nutritional profile requires comparing them to similar processed cheeses; for instance, a look at american cheese nutrition facts reveals a different fat and sodium content. Ultimately, the nutritional value of mozzarella sticks hinges on portion size and the overall dietary context, just as with any other processed food.
Mozzarella Cheese Sticks in Various Diets
Mozzarella cheese sticks can find a place in some, but not all, dietary approaches. Within vegetarian diets, they can serve as a convenient source of protein and calcium, although mindful portion control is essential due to the fat and sodium content. However, their suitability within a ketogenic diet is more nuanced. While the high fat content aligns with ketogenic principles, the relatively high carbohydrate content from the breading may disrupt ketosis in some individuals.
Therefore, careful consideration of the nutritional information and individual metabolic responses is crucial. For example, selecting cheese sticks with a lower carbohydrate breading or opting for unbreaded mozzarella sticks can better accommodate a ketogenic diet.
Ingredient Analysis and Additives
The seemingly simple mozzarella cheese stick holds within it a complex tapestry of ingredients, a microcosm reflecting our modern food system. Understanding these components—their origins, their purposes, and their potential impacts—is crucial to making informed choices that align with our personal values and health goals. This analysis delves into the common ingredients and additives, exploring their roles and the subtle yet significant ways they shape the nutritional profile and overall experience of this popular snack.
Commercially produced mozzarella cheese sticks often contain a surprising array of ingredients beyond just cheese. The seemingly straightforward nature of the product belies a complex manufacturing process involving several additives designed to enhance texture, shelf life, and overall appeal. This section will illuminate the common components found in most brands and explore the potential consequences of their inclusion.
Common Ingredients in Mozzarella Cheese Sticks
The ingredient list on a package of mozzarella cheese sticks often reads like a scientific formula. While the primary ingredient is usually mozzarella cheese, the supporting cast plays a vital role in determining the final product’s texture, taste, and shelf life. A closer examination reveals a common pattern across various brands.
- Mozzarella Cheese: This is the star ingredient, though its percentage can vary significantly between brands. The type of mozzarella used—part-skim, whole milk, or a blend—influences the fat content and overall nutritional value.
- Water: Added to adjust the moisture content and consistency of the cheese mixture.
- Whey: A byproduct of cheese production, often added to improve texture and binding.
- Milk Solids: Contribute to the cheese’s creamy texture and richness.
- Modified Food Starch: Acts as a thickener and stabilizer, preventing separation and maintaining a desirable texture.
- Salt: Enhances flavor and acts as a preservative.
- Soybean Oil or Other Vegetable Oils: Used in the breading process to create a crispy coating.
- Breading (Flour, Breadcrumbs, etc.): Provides the characteristic outer crust.
- Leavening Agents (Baking Powder, Baking Soda): Help create a light and airy breading.
- Preservatives (e.g., Sorbic Acid, Potassium Sorbate): Extend the shelf life of the product, preventing spoilage.
- Flavor Enhancers (e.g., Monosodium Glutamate (MSG)): Enhance the savory taste of the cheese sticks.
- Enzymes: Used in the cheese-making process to aid in coagulation and texture development.
Impact of Additives and Processing Methods
The additives and processing methods employed in the production of mozzarella cheese sticks significantly impact their nutritional value and potential health implications. While some additives are generally recognized as safe, their cumulative effect and long-term consequences remain a subject of ongoing research and debate. The delicate balance between palatability, shelf-life, and nutritional integrity is a constant challenge for food manufacturers.
For instance, the high sodium content from salt and the presence of saturated fat from cheese and oil contribute to concerns about cardiovascular health. Excessive consumption of processed foods containing these additives can increase the risk of various health problems. The use of modified food starches, while enhancing texture, may also raise questions about their potential impact on gut health and blood sugar levels.
Furthermore, the deep-frying process often employed adds significant calories and unhealthy fats.
Comparison of Brand Ingredients
A comparative analysis of ingredient lists from different brands of mozzarella cheese sticks reveals considerable variation. Some brands may emphasize natural ingredients and minimize additives, while others prioritize cost-effectiveness and shelf life, resulting in longer ingredient lists with more additives. For example, one brand might use a higher percentage of real mozzarella cheese compared to another, leading to a difference in taste and nutritional profile.
Similarly, some brands might utilize different types of oils or starches, influencing the overall fat and carbohydrate content. Consumers should carefully examine ingredient lists and nutritional information panels to make informed decisions based on their individual dietary needs and preferences. This mindful approach allows for a conscious engagement with the food choices we make, aligning consumption with our values and health goals.
FAQ Explained
Are mozzarella cheese sticks gluten-free?
Not always! Check the ingredient list; some brands might contain wheat or gluten-containing ingredients.
Can I bake mozzarella cheese sticks instead of frying them?
Totally! Baking significantly reduces the fat content compared to deep frying. Just make sure to check the cooking time and temperature on the package.
Are mozzarella cheese sticks a good source of protein?
They offer some protein, but it’s not their primary nutritional highlight. They’re more of a fat and carbohydrate source.
What are some healthier alternatives to mozzarella cheese sticks?
Consider homemade versions using whole wheat breading and part-skim mozzarella, or opt for veggie sticks with hummus or air-popped popcorn for a lower-calorie snack.








